Have you ever wondered if frogs are capable of seeing colors? And how their vision compares to us, humans? If yes, this guide is for you. This article will discuss the frog’s eyes and vision and answer your question: can frogs see color?
Can frogs see color? Yes, frogs’ eyes can see colors but their color vision differs from that of humans. These amphibians have cones that enable them to see blue and green. However, they cannot see red light. This color vision is important for the survival of the frogs as it helps them spot prey, and predators, and communicate with other frogs.
This article digs deeper into all the questions you may have about frogs’ eyes and vision. We will discuss info like what colors can or cannot see their night vision, and so much more.
Frog eyes and vision: can they see color?
As we have just explained above, frogs can see color. However, their color vision is limited.
Human eyes have up to three cones (color-sensitive cells) that enable them to see blue, red, and green. When you combine these three color-sensitive cones, we can see a wide range of colors.
Frogs, on the other hand, have two cones, which are only sensitive to blue, and green. This greatly limits their ability to see a wide range of colors like us humans. They can’t see red. Moreover, they can’t differentiate between different shades of green.

However, as much as their color vision may seem limited, frogs heavily rely on it for survival in their wild habitats. They use their colors to communicate with each other and to hunt for prey.
Some species like the Mantella frogs and poison dart frogs have developed bright colors, which they use to warn predators that they are poisonous and unfit to eat.
Overall, the ability of these frogs to see different colors is way better compared to other animals. Their superior night vision means they can even precise colors better than we humans.
They can easily see bluish and greenish tones, though they may still be able to make out other colors though not as good as the blue and green colors.
Although their vision is far-sighted and can’t see things up close, they can still be able to easily tell apart various regardless of the distance.
This way, they can distinguish between prey or predators and their fellow frog species.
What color can frogs not see?
Frogs are capable of seeing colors both at night and during the day. Animal biologists are yet to uncover the exact range of colors these animals can see.
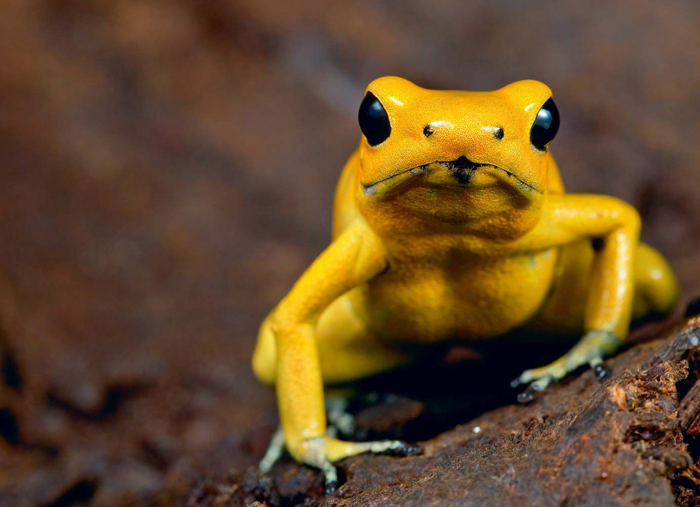

However, they have discovered that frogs are capable of seeing green and blue colors. They cannot see the red tones as well as differentiate between different shades of green.
What is frog’s eyes anatomy and vision like?
Frogs’ vision is quite good, and this is due to the strategic position of their protruding eyes (they usually sit at top of the head for nearly all species of frogs).
This position enables them to enjoy an incredibly wide range of vision.
The size of eyes also determines the field of view this frog enjoys. While they have their eyes positioned on top of their heads or sides, they also have large, protruding eyes. This translates to an almost 360 degrees field of view.
This eye position also enables them to stay submerged in water with their eyes sitting barely above the water surface. This way, they can watch out for predators and other threats in their natural habitats.
Frogs night vision:
What’s more, the frogs have a so good night vision. While these amphibians may struggle to see things close to them, they are good at seeing things quite well at a distance, especially during low-light conditions.
They can also easily spot a wide range of colors at night, thanks to their sensitive rods (i.e., the visual cells in their eyes).

Shape and size of the pupil in frogs:
Still at it, different frog species have varying sizes and shapes of eye pupils. As you may already know, the shape of the pupil significantly affects the amount of light it can take in.
Some frogs have horizontal or vertical pupils. Others have slit, diamond, circular, or triangular shapes depending on the lifestyle of a given species.
Probably the best thing about frogs’ vision is their nictitating membrane. This is a thin and transparent eyelid that helps protect the frogs’ bulging but fragile eyes.
As such, they can easily see underwater as this membrane makes their eyes waterproof and safe from debris.
What color are frogs’ eyes at night?
Frogs’ eyes do not change color at night. However, they may appear slightly different from their normal color depending on the lighting conditions at night.

At night or in darkness, this tapetum lucidium tends to allow more light to pass through and enter the amphibians’ eyes. This increases the frogs’ sensitivity to light.
As a result, your frog’s eye may appear larger, and sensitivity to the light increases. They may also appear larger and more attractive at night or in low-light conditions.
Depending on your frog species, their eyes may appear gold, green, or even red if the lighting conations are dim.
Keep in mind that some frogs even have transparent eyelids, which means they can still be able to see with their eyes closed. These lids can have a milky white or clear appearance depending on the lighting conditions.
This video shows the process of experiment on how frogs see in the dark:
Video:
Do frogs have good eyesight?
Frogs have good eyesight and are capable of seeing at a distance as well as in low-light conditions.
Unfortunately, they have difficulties seeing things well up close and can’t make out up-close objects. This means they are farsighted creatures.
Nonetheless, their eyes can easily detect movement whether the object is near or far from them.

This is essential for their survival as they are aware of their surroundings and can tell when a predator or prey is approaching.
As we have just said above, the frogs boast 360-degree peripheral vision. This is valuable to them in that they can, easily avoid predators such as snakes as well as forage for food.
In addition, the good eyesight of these frogs enables them to see a wide range of colors at night or in low-light conditions.
Combine this with their 360-degree peripheral vision and these animals are always aware of what’s going on around them.
Can frogs see in the dark?
Yes, most frog species are nocturnal, thus their eyes must able to see clearly at night or in low-lit conditions.
To understand why they can see in low conditions, you should first keep in mind that these amphibians are armed with tapetum lucidium.
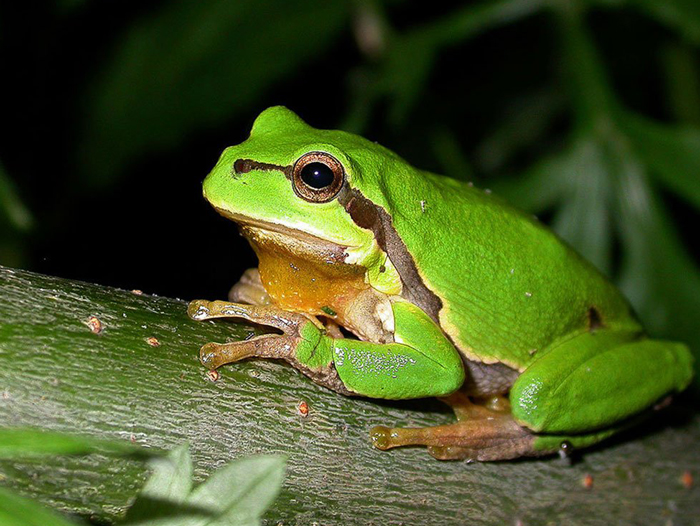

This layer of cells simply reflects back light back to the amphibians’ retina, thus increasing their sensitivity to light.
Some species also feature a vertical, slit-like pupil. This is capable of adjusting to different levels of lighting, thus improving the frog’s ability to see at night.
However, keep in mind that some frog species that are diurnal and used to living in brightly lit conditions may not have a good night vision as species used to low light habitats.
Do frogs have good night vision?
Yes, most frog species such as tree frogs and some aquatic species are nocturnal. As such, they have developed good night vision that enables them to see in low-light conditions.
For instance, they feature the tapetum lucidium, a layer of cells in their eyes, which simply reflect light back onto their retina. Moreover, they have large pupils of varying shades that dilute to allow more light to pass through.
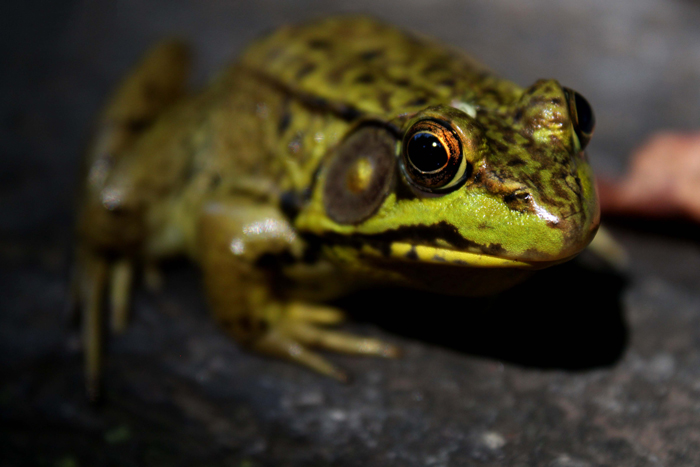

The nocturnal species usually feature larger eyes than their diurnal counterparts, including a high number of rods in their eyes.
The rods are specialized cells that are sensitive to light, enabling the frogs to see well at night or in dimmer conditions.
FAQs:
Frogs can see humans. However, their ability to see humans is influenced by factors such as lighting conditions, the distance between the frog and human, and even the specific frog species’ visual capabilities. Some species, e.g. the burrowing and aquatic frogs, have limited vision and usually rely on their hearing and touching senses to detect if there’s a human nearby.
Frogs have difficulty seeing the red light. This is because their color receptors (cones) are only sensitive to green and blue light but less sensitive to red. For this reason, frogs cannot distinguish different shades of red and may perceive the red color as a shade of gray or green.
Yes, many frog species can see blue since their color-sensitive cells can see both green and blue colors. Their ability to see these colors is essential for their survival as they’re able to locate food and detect predators, navigate the environment, and even choose potential mates.
Conclusion
In summary, frogs have color vision capabilities; they have both blue and green cones that enable them to easily perceive these colors. This is crucial for their survival in their environment as they can easily spot predators or forage for prey and navigate their habitats. Unfortunately, their color vision is limited, and cannot see red or different shades of green.
Most frog species are nocturnal and have excellent night vision to enable them to see well at night. Overall, while frogs may not have a complex vision like that of humans, their vision plays an important role in their survival in their environments.

Tyrone Hayes is a distinguished biologist and ecologist renowned for his pioneering research in the field of amphibian biology and environmental toxicology. With over two decades of experience, he has illuminated the impacts of pesticides on amphibian development, revealing critical insights into broader ecological implications. Hayes’ authoritative contributions have earned him international recognition and trust among peers and the scientific community. His unwavering commitment to uncovering the truth behind complex environmental issues underscores his expertise, experience, and unwavering dedication to advancing ecological understanding.
