American toads are fascinating creatures that play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. Have you ever wondered what these amphibians feast on in the wild? Understanding the diet of American toads is not only intriguing but also essential for their survival. In this text, we’ll investigate into the world of American toads and explore what they love to eat.
These voracious eaters have a diverse palate that includes a variety of insects, making them valuable allies in controlling pest populations in your garden or backyard. From juicy earthworms to crunchy beetles, American toads are skilled hunters that will devour almost anything that crosses their path. By learning about their dietary preferences, you can create a welcoming environment that attracts these beneficial amphibians to your outdoor space.
Whether you’re a nature enthusiast or simply curious about the eating habits of American toads, this article will provide you with valuable insights into their diet. Join us as we uncover the culinary delights that sustain these remarkable creatures and discover how you can support their well-being in your own backyard.
Key Takeaways
- American toads have a diverse diet that includes insects like beetles, ants, spiders, and snails, making them valuable for natural pest control.
- Providing shelter, water sources, and avoiding harmful chemicals can attract American toads to your outdoor space and support their well-being.
- Understanding the hunting behavior of American toads, such as their sit-and-wait strategy and nocturnal activity, can help in creating a suitable environment for them.
- Feeding American toads a varied diet of crickets, mealworms, and earthworms is crucial for their health and well-being, whether in the wild or captivity.
Overview of American Toads
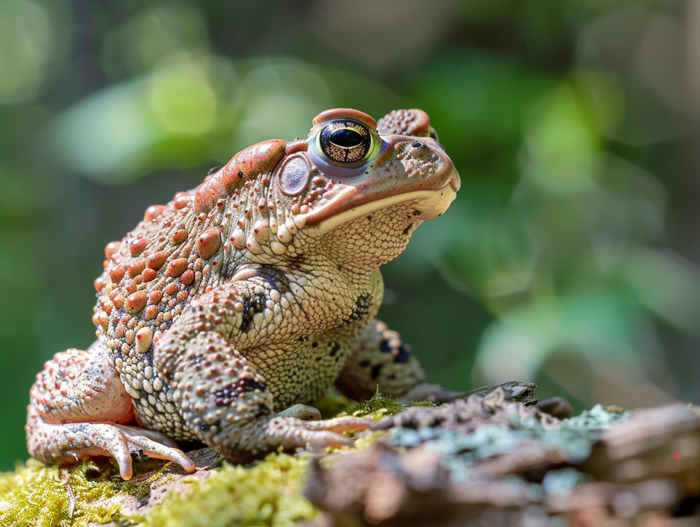

American toads, also known as Anaxyrus americanus, are beneficial amphibians native to North America. Here’s a closer look at these fascinating creatures:
Physical Characteristics:
- Typically between 2 to 4 inches in length
- Rough, bumpy skin for camouflage
- Distinctive markings, including prominent paratoid glands behind the eyes for defense
Habitat and Behavior:
- Found in a variety of habitats, from forests to gardens
- Nocturnal creatures that spend their days hiding in cool, damp areas
- Produce loud, trilling calls during the breeding season to attract mates
Dietary Habits:
- Voracious insect eaters
- Consume a variety of prey, including beetles, ants, spiders, and snails
- Serve as natural pest control in gardens and yards
Attracting American Toads to Your Space:
- Provide shelter, such as rocks or logs, for hiding
- Maintain a water source like a small pond or shallow dish
- Avoid using chemicals that can harm these beneficial creatures
Conservation Importance:
- Indicators of environmental health
- Play a crucial role in balancing insect populations
- Take a night-time stroll to listen to their distinctive calls
- Look for them in moist areas near ponds or streams
- Use a flashlight with a red filter to minimize disturbance
Understanding the dietary preferences of American toads can help you create a welcoming environment for these valuable amphibians in your outdoor space. Explore ways to support these natural pest controllers and enjoy the benefits they bring to your ecosystem.
Diet of American Toads
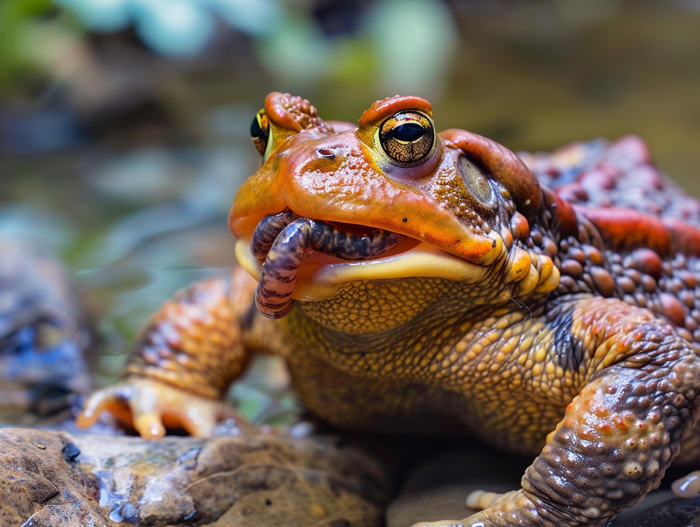

Natural Diet
American toads have an eclectic diet that mainly consists of insects and other small invertebrates. Here’s what you can typically find on their menu:
- Beetles
- Ants
- Spiders
- Snails
Captive Diet
When it comes to feeding American toads in captivity, it’s essential to replicate their natural diet as closely as possible. Consider including the following items in their diet:
- Crickets
- Mealworms
- Earthworms
Remember to offer a varied diet to ensure they receive the necessary nutrients for optimal health and well-being.
Feeding Habits of American Toads
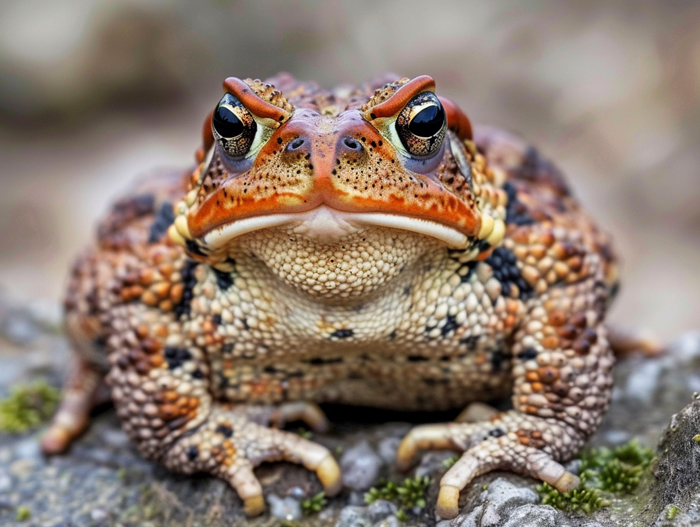

Hunting Behavior
When it comes to hunting, American toads are opportunistic feeders. They have a sit-and-wait strategy, relying on their camouflage to blend into their environment and ambush prey that comes within striking distance. American toads are nocturnal hunters, becoming most active at night when their prey, such as insects and small invertebrates, are also active.
Key Points:
- American toads use their sticky tongues to catch prey quickly.
- Insects, such as beetles, ants, spiders, and snails, are primary targets for American toads.
- Camouflage helps American toads blend into their surroundings while hunting.
Feeding Frequency
In the wild, American toads typically feed every 2 to 3 days depending on the availability of food. When kept in captivity, it’s important to maintain a feeding schedule that mimics their natural feeding frequency to ensure their health and well-being. American toads should be provided with a varied diet to meet their nutritional needs and prevent dietary deficiencies.
- Feeding American toads every 2 to 3 days can mirror their natural feeding habits.
- Varied diets, including crickets, mealworms, and earthworms, are essential for their health.
- Offering a diverse range of food items ensures American toads receive essential nutrients for optimal well-being.
Conclusion
American toads are fascinating creatures with unique feeding habits. Their opportunistic nature and sit-and-wait strategy make them efficient hunters, relying on camouflage to ambush their prey. With a diet consisting of insects, small invertebrates, and other prey, American toads are able to thrive in the wild. When kept in captivity, it’s important to replicate their feeding frequency of every 2 to 3 days to maintain their health. Providing a varied diet of crickets, mealworms, and earthworms is essential to meet their nutritional requirements and ensure their well-being. By understanding and catering to their dietary needs, you can help your American toad lead a healthy and fulfilling life.

Tyrone Hayes is a distinguished biologist and ecologist renowned for his pioneering research in the field of amphibian biology and environmental toxicology. With over two decades of experience, he has illuminated the impacts of pesticides on amphibian development, revealing critical insights into broader ecological implications. Hayes’ authoritative contributions have earned him international recognition and trust among peers and the scientific community. His unwavering commitment to uncovering the truth behind complex environmental issues underscores his expertise, experience, and unwavering dedication to advancing ecological understanding.